DSL
DSL
创建文档
PUT student/_doc/1
{
"name": "test 1",
"age": 22
}
POST student/_doc
{
"name": "test 2",
"age": 21
}
// 批量创建,注意一个花括号一行
PUT student/_bulk
{"index":{"_id": 2}}
{"name": "koston", "age": 24}
{"index":{"_id":3}}
{"name": "koston zhuang", "age": 20}
{"index":{"_id":4}}
{"name": "kostonzhuang", "age": 20}提示
PUT 请求中,最后需要包含唯一性标识,POST 可以不包含,将会自动生成。
基础查询
查询所有
GET student/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {
}
},
"sort": [
{
"age": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}match_all 表示查询所有数据,sort 表示按照什么字段排序。
查询结果如下图:
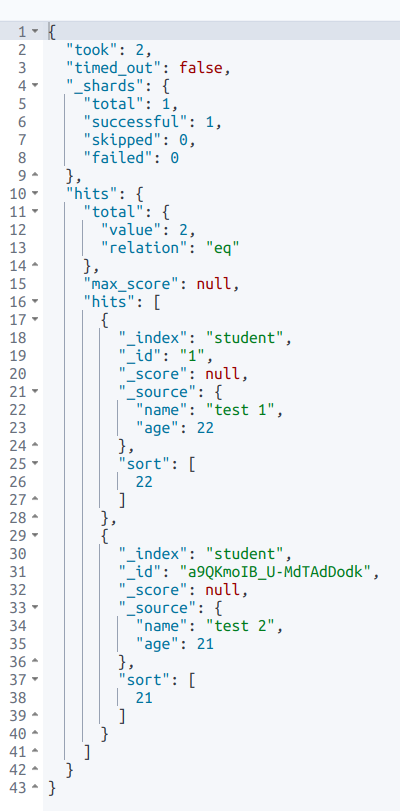
took:Elasticsearch 运行查询所花费的时间(以毫秒为单位)。timed_out:搜索请求是否超时。_shards:搜索了多少个碎片,以及成功,失败或跳过了多少个碎片的细目分类。max_score:找到的最相关文档的分数。hits.total.value:找到了多少个匹配的文档。hits.sort:文档的排序位置(不按相关性得分排序时)。hits._score:文档的相关性得分(使用 match_all 时不适用)。
分页查询
利用 from 和 size 实现分页。
GET student/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {
}
},
"sort": [
{
"age": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
],
"from": 0,
"size": 1
}指定字段查询
GET student/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "koston test"
}
}
}因为 Elasticsearch 是分词索引的,例如如果值中包含空格则会被拆成多个分词,又因为 match 也是分词查询的,因此上面的查询结果将不会包含 name 为 kostonzhuang 的结果,但会包含分词中有 koston 或者 test 的结果。
查询段落匹配
如果不想分词查询:
GET student/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"name": "koston zhuang"
}
}
}部分字段查询
GET student/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"name": "koston"
}
},
{
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 23
}
}
}
]
}
},
"_source": ["age"]
}复合查询
布尔查询
Bool 查询语法有以下特点:
- 子查询可以任意顺序出现。
- 可以嵌套多个查询,包括 bool 查询。
- 如果 bool 查询中没有 must 条件,should 中必须至少满足一条才会返回结果。
bool 查询包含四种操作符:分别是 must, should, must_not, filter。他们均是一种数组,数组里面是对应的判断条件。
- must:必须匹配。贡献算分。
- must_not:过滤子句,必须不能匹配,但不贡献算分。
- should:选择性匹配,至少满足一条。贡献算分。
- filter:过滤子句,必须匹配,但不贡献算分。
GET student/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"name": "koston"
}
}
],
"must_not": [
{
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 10,
"lte": 20
}
}
}
]
}
}
}对于 should 匹配,minimum_should_match 可以控制返回的文档必须满足多少个 should 条件,例如设置此参数为 2,则文档必须同时满足两个及以上的 should 条件才能被匹配。
GET member/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"term": {
"isActivated": {
"value": false
}
}
},
{
"term": {
"isDeleted": {
"value": true
}
}
}
],
"minimum_should_match": 2
}
}
}提高查询
不同于布尔查询,布尔查询中只要一个子查询条件不匹配那么就不会出现在结果中,提高查询 boosting query 则是降低显示的权重,即评分。
提高查询有三个参数:
- positive:必填,query object,所有返回的文档都满足此条件。
- negative:必填,query object,满足此条件的文档的评分将会降低。
- negative_boost:必填,介于 0 到 1 之间的浮点数,用来降低评分。
如果一个文档同时满足两个查询条件,那么会首先根据 positive 计算评分,然后根据 negative_boost 降低评分。
// 分词查询,对于分词包含 koston 的提高评分,包含 zhuang 的降低评分
GET student/_search
{
"query": {
"boosting": {
"positive": {
"match": {
"name": "koston"
}
},
"negative": {
"match": {
"name": "zhuang"
}
},
"negative_boost": 0.5
}
}
}固定分数查询
查询某个条件时,固定的返回指定的 score。
GET student/_search
{
"query": {
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 22
}
}
},
"boost": 1.2
}
}
}- filter:查询条件,返回的文档必须满足这个条件,不计分。
- boost:可选的,浮点数,作为查询得到的每个文档的分数,默认值为 1.0。
最佳匹配查询
首先插入数据:
POST /test-dsl-dis-max/_bulk
{ "index": { "_id": 1 }}
{"title": "Quick brown rabbits","body": "Brown rabbits are commonly seen."}
{ "index": { "_id": 2 }}
{"title": "Keeping pets healthy","body": "My quick brown fox eats rabbits on a regular basis."}此时,如果需要搜索 标题或者内容中包含 Brown fox 的结果,如果使用布尔查询:
GET /test-dsl-dis-max/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{ "match": { "title": "Brown fox" }},
{ "match": { "body": "Brown fox" }}
]
}
}
}因为第一条文档的标题和内容中对于查询的内容的评分都是大于 0 的,最终两个 should 的评分之和大于第二条,但是实际上第二条记录的优先级应当更高,因此就需要引入最佳匹配查询,将任意和任一查询匹配的文档作为结果返回,但是只把最佳匹配的评分作为查询的评分返回。
GET /test-dsl-dis-max/_search
{
"query": {
"dis_max": {
"queries": [
{ "match": { "title": "Brown fox" }},
{ "match": { "body": "Brown fox" }}
],
"tie_breaker": 0
}
}
}评分计算:分数 = 第一个匹配条件分数 + tie_breaker * 第二个匹配的条件的分数……
Function Score
TODO:
全文搜索
首先创建一些数据:
POST /test-dsl-match/_bulk
{ "index": { "_id": 1 }}
{ "title": "The quick brown fox" }
{ "index": { "_id": 2 }}
{ "title": "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog" }
{ "index": { "_id": 3 }}
{ "title": "The quick brown fox jumps over the quick dog" }
{ "index": { "_id": 4 }}
{ "title": "Brown fox brown dog" }match
match 查询中,对于多个分词会分多次 term 查询然后将结果使用布尔查询组合起来,默认情况下,满足任一分词的结果都会出现在最终结果里,也可以指定 operator 要求每个分词都满足:
GET test-dsl-match/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": {
"query": "quick brown",
"operator": "and"
}
}
}
}query:text、number、boolean、date 类型的值。
auto_generate_synonyms_phrase_query:表示在执行 match 查询时,是否自动将同义词生成为短语查询,默认值为 true,例如如果同义词中包含 tv 和 television,那么如果 query 内容为 tv stand,那么这个查询会被转换为
(tv stand) OR (television stand)的短语查询,这意味着只有 tv 和 stand 紧密出现时才会被匹配,如果设置此字段为 false,那么上面的查询将被转换为tv OR television AND stand,这将返回包含 tv 或 television 并且包含 stand 的文档而不需要它们紧密出现。fuzziness:指定查询的模糊度,默认值为 AUTO,另外可以使用整数明确指定一个值,例如设置此值为 1,那么在查询条件的基础上,最多只需要一次编辑操作(插入、删除或者替换一个字符)就能将查询词变成某个文档的此字段才会被匹配。
现在有一个 name 为 Antelopeshag 的文档,如果查询词为 Antelopesh,即需要两次编辑的情况下,如果 fuzziness 值小于 2 则无法查到。
GET member/_search { "query": { "match": { "name": { "query": "Antelopesh", "fuzziness": 2 } } } }max_expansions:当开启了同义词转换时控制同义词扩展的数量。
prefix_length:当进行模糊搜索时,设置前多少个字符进行精确匹配。
fuzzy_transpositions:当进行模糊匹配时,此参数决定了将两个相邻字符互换是否会被视作编辑操作,默认值为 true,此时如果互换两个字母就能匹配则不会占用 fuzziness。
fuzzy_rewrite:
lenient:设置是否对一些异常情况进行宽容处理,例如尝试在整数字段上做文本查询,默认情况下这将会报错,但是可以通过此参数控制 es 尽量进行查询而不报错。
operator:设置多个查询词的关系,例如查询内容是 "this is test",默认情况下只要文档对应字段包含这三个单词的任一个即可,如果指定为 and,那么必须同时包含这三个词。
zero_terms_query:此参数决定当所有的查询词都被过滤掉的行为,默认值为 none,意味着不会返回任何结果,如果设置为 all 则会返回所有文档。
minimum_should_match:此参数决定了一个查询应该匹配多少个词才算匹配,接收整数或者百分比。
match_bool_prefix 对于查询字符串的最后一个词,会执行一个 prefix 查询,对于其他词会执行 match 查询,例如有下面这样的例子:
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"match_bool_prefix" : {
"message" : "quick brown f"
}
}
}等价于:
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"bool" : {
"should": [
{ "term": { "message": "quick" }},
{ "term": { "message": "brown" }},
{ "prefix": { "message": "f"}}
]
}
}
}match_phrase 用于执行短语匹配,当希望找到一整个短语而不是独立的单词可以使用,查询中的词必须以相同的顺序出现在文档中,并且它们之间不能有其他词。下面的例子中 title 字段包含 quick brown fox 的文档将被返回。
GET test-dsl-match/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title": {
"query": "quick brown fox"
}
}
}
}match_phrase_prefix 相比于 match_phrase,执行短语查询的同时允许最后一个词做前缀匹配。
GET test-dsl-match/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase_prefix": {
"title": {
"query": "quick brown f"
}
}
}
}combined_fields 可以在多个字段上进行查询,例如:
{
"query": {
"combined_fields": {
"query": "quick brown fox",
"fields": ["title^2", "content"]
}
}
}在这个示例中,查询将会在 title 字段和 content 字段上进行,其中 title 权重设置为 2,它的匹配度将比 content 字段更高。
multi_match 会在多个字段上进行全文匹配,任一字段匹配的文档就会加入结果:
{
"query": {
"multi_match" : {
"query": "Will Smith",
"fields": [ "title^2", "*_name" ]
}
}
}可以通过 type 字段指定类型:
- best_fields:默认类型,为每个字段生成 dis_max 查询,从中选择得分最高的结果,适合处理查询字符串与某个字段的全文非常匹配的情况。
- most_fields:为每个字段生成一个查询,将所有的查询组合为一个 should 布尔查询,也就是说任一字段匹配都会被返回。
- cross_fields:这种类型是为了处理在多个字段中分散存储的文本,比如名字的姓和名分别存储在两个字段中。这种类型会把所有字段当作一个大的字段进行查询,并对每个字段的查询结果进行合并。
- phrase:在每个字段上做 match_phrase 查询。
- phrase_prefix:在每个字段上做 match_phrase_prefix 查询。
- bool_prefix:在每个字段上做 match_bool_prefix 查询。
query string
query_string 类似 SQL 语句:
GET test-dsl-match/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"default_field": "title",
"query": "(lazy dog) OR (brown dog)"
}
}
}Term
准备数据:
PUT /test-dsl-term-level
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"programming_languages": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"required_matches": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
}
POST /test-dsl-term-level/_bulk
{ "index": { "_id": 1 }}
{"name": "Jane Smith", "programming_languages": [ "c++", "java" ], "required_matches": 2}
{ "index": { "_id": 2 }}
{"name": "Jason Response", "programming_languages": [ "java", "php" ], "required_matches": 2}
{ "index": { "_id": 3 }}
{"name": "Dave Pdai", "programming_languages": [ "java", "c++", "php" ], "required_matches": 3, "remarks": "hello world"}字段是否存在:
GET test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"exists": {
"field": "title"
}
}
}id 查询:
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": [3, 1]
}
}
}前缀查询:
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"name": {
"value": "Jan"
}
}
}
}提示
可以通过设置 value 的同级属性 case_insensitive 为 true 忽略大小写。
分词匹配 term、terms:
// 基础查询
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"programming_languages": "php"
}
}
}
// 多分词匹配,它们是或关系
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"terms": {
"programming_languages": ["php","c++"]
}
}
}通配符 wildcard:
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"name": {
"value": "D*ai",
"boost": 1.0,
"rewrite": "constant_score"
}
}
}
}范围 range:
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"required_matches": {
"gte": 3,
"lte": 4
}
}
}
}提示
可以通过 relation 字段(与 gte 同级)控制返回的文档和筛选范围的关系:
- INTERSECTS:默认值,字段值和范围有交集就返回。
- CONTAINS:字段值包含了要查询的范围就返回。
- WITHIN:字段值完全在要查询的范围内就返回。
正则匹配 regexp:
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"regexp": {
"name": {
"value": "Ja.*",
"case_insensitive": true
}
}
}
}模糊匹配 fuzzy:
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"remarks": {
"value": "hell"
}
}
}
}提示
和 match 查询类似,fuzzy 查询支持设置 fuzziness、max_expansions、prefix_length(均和 value 同级)。
模糊匹配支持下面几种情况:
- 更改字符(box->fox)。
- 删除字符(black->lack)。
- 插入字符(sic->sick)。
- 转置两个相邻字符(act->cat)。
地理坐标查询
准备数据:
PUT /my_locations
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"pin": {
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "geo_point"
}
}
}
}
}
}
PUT /my_locations/_doc/1
{
"pin": {
"location": {
"lat": 40.12,
"lon": -71.34
}
}
}
PUT /my_geoshapes
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"pin": {
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "geo_shape"
}
}
}
}
}
}
// 一个四边形,第一个点必须和最后一个点重合
PUT /my_geoshapes/_doc/1
{
"pin": {
"location": {
"type" : "polygon",
"coordinates" : [[[13.0 ,51.5], [15.0, 51.5], [15.0, 54.0], [13.0, 54.0], [13.0 ,51.5]]]
}
}
}geo_bound_box
使用 geo_bounding_box 来过滤 geo_point 类型的数据,定义 geo_bounding_box 查询需要执行两个对角的坐标(左上角和右下角):
GET my_locations/_search
{
"query": {
"geo_bounding_box": {
"pin.location": {
"top_left": {
"lat": 40.73,
"lon": -74.1
},
"bottom_right": {
"lat": 40.01,
"lon": -71.12
}
}
}
}
}两个对角坐标也可以用 GeoJSON 格式([lon, lat])表示:
GET my_locations/_search
{
"query": {
"geo_bounding_box": {
"pin.location": {
"top_left": [-74.1, 40.73],
"bottom_right": [-71.12, 40.01]
}
}
}
}geo_distance
指定一个坐标和距离,筛选距离此坐标在指定距离内的点。
GET my_locations/_search
{
"query": {
"geo_distance": {
"distance": "200km",
"pin.location": {
"lat": 40,
"lon": -70
}
}
}
}距离单位参考Distance Units
geo_grid
这是一种特殊类型的聚合,它用于聚合 geo_point 字段,这些字段表示地理位置(例如,经纬度坐标)。在 geohash_grid 聚合中,地图被分割为多个小格子,每个格子有一个唯一的 geohash,geohash是地理位置的一种精确且有效的编码方式。
对于每个小格子,Elasticsearch会统计它包含的文档数量,然后返回这些信息。这可以让你了解哪些地理位置区域有大量文档,或者哪些区域有少量文档。
precision 参数控制 geohash 的精度,值越大,地理位置的精度越高,小格子的大小越小。精度可以是1到12的整数,1表示最低的精度,12表示最高的精度。返回的结果包含每个 geohash 和对应的文档数。
准备数据:
PUT /my_locations
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "geo_point"
}
}
}
}
PUT /my_locations/_doc/1?refresh
{
"location" : "POINT(4.912350 52.374081)",
"city": "Amsterdam",
"name": "NEMO Science Museum"
}
PUT /my_locations/_doc/2?refresh
{
"location" : "POINT(4.405200 51.222900)",
"city": "Antwerp",
"name": "Letterenhuis"
}
PUT /my_locations/_doc/3?refresh
{
"location" : "POINT(2.336389 48.861111)",
"city": "Paris",
"name": "Musée du Louvre"
}执行查询:
GET my_locations/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"locations": {
"geohash_grid": {
"field": "location",
"precision": 2
}
}
}
}根据上一步的结果可以再次查询每个 grid
GET my_locations/_search
{
"query": {
"geo_grid": {
"location": {
"geohash": "u0"
}
}
}
}geo_polygon
给出多边形的顶点,筛选在这个多边形内的文档。
{
"query": {
"geo_polygon": {
"person.location": {
"points": [
{"lat": 40, "lon": -70},
{"lat": 30, "lon": -80},
{"lat": 20, "lon": -90}
]
}
}
}
}提示
此查询只在 geo_point 字段上有效。
geo_shape
给出多个点,查找与这些点组成的多边形相交、包含等关系的 geo_shape 或 geo_point。
{
"query": {
"geo_shape": {
"location": {
"shape": {
"type": "Polygon",
"coordinates": [[[30, 10], [40, 40], [20, 40], [10, 20], [30, 10]]]
},
"relation": "INTERSECTS"
}
}
}
}relation 的取值:
- INTERSECTS:相交。对于geo_point字段,这意味着所有位于给定形状内部或边界上的点。
- WITHIN:完全在给定形状内的 geo_shape。对于geo_point字段,这意味着所有位于给定形状内部的点,不包括边界上的点。
- CONTAINS:完全包含给定形状的 geo_shape。对于geo_point字段,这个参数没有意义,因为点不能“包含”其他点或形状。
- DISJOINT:与给定形状不相交的 geo_shape。对于geo_point字段,这意味着所有位于给定形状外部的点。
Joining Query
Nested
nested 查询类似于 MongoDB 中的 $elemMatch,用于查询对象数组中的完整符合条件的情况,首先建立索引并创建数据:
put order
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "text"
},
"createdAt": {
"type": "date"
},
"products": {
"type": "nested",
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "text"
},
"price": {
"type": "long"
},
"total": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
}
}
}
POST order/_doc
{
"id": "001",
"createdAt": "2023-07-03T08:04:54.687+00:00",
"products": [
{
"id": "p_001",
"price": 100,
"total": 5
},
{
"id": "p_002",
"price": 123,
"total": 2
}
]
}
POST order/_doc
{
"id": "002",
"createdAt": "2023-07-04T01:53:34.034+00:00",
"products": [
{
"id": "p_001",
"price": 100,
"total": 3
},
{
"id": "p_002",
"price": 123,
"total": 1
}
]
}现在,查询购买了两个 p_002 商品的订单:
GET order/_search
{
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "products",
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"products.total": {
"value": 2
}
}
},
{
"term": {
"products.id": {
"value": "p_002"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
}提示
可以在 nested 中指定 ignore_unmapped 参数(与 path 同级)来忽略路径不匹配导致的错误。
Has child
首先创建数据:
PUT join_index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"my_id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"my_join_field": {
"type": "join",
"relations": {
"question": "answer"
}
}
}
}
}
PUT join_index/_doc/1?refresh
{
"my_id": "1",
"text": "This is a question",
"my_join_field": "question"
}
PUT join_index/_doc/2?refresh
{
"my_id": "2",
"text": "This is another question",
"my_join_field": "question"
}
PUT join_index/_doc/3?refresh&routing=1
{
"my_id": "3",
"text": "This is an answer",
"my_join_field": {
"name": "answer",
"parent": "1"
}
}
PUT join_index/_doc/4?refresh&routing=1
{
"my_id": "4",
"text": "This is another answer",
"my_join_field": {
"name": "answer",
"parent": "1"
}
}执行查询:
GET join_index/_search
{
"query": {
"has_child": {
"type": "answer",
"query": {
"term": {
"my_id": {
"value": "3"
}
}
},
"min_children": 1,
"max_children": 2
}
}
}- type:指定 join 关系中的子文档的关系名,在上面的索引中是 "answer"。
- query:指定在子文档上执行的查询记录,如果有一个子文档符合条件,那么父文档将被返回。
- max_children:指定最多有多少个子文档匹配,如果一个父文档的匹配的子文档的数量超出此值,查询结果将不会包含此父文档。
- min_children:指定至少有多少个子文档匹配,如果一个父文档的匹配的子文档的数量小于此值,查询结果将不会包含此父文档。
Has Parent
类似于 has_child 查询。
GET join_index/_search
{
"query": {
"has_parent": {
"parent_type": "question",
"query": {
"term": {
"my_id": {
"value": "1"
}
}
}
}
}
}Parent ID
通过父文档的 id 进行查询。
GET join_index/_search
{
"query": {
"parent_id": {
"type": "answer",
"id": 1
}
}
}- type:子文档在关系中的名字,这里是 answer。
- id:父文档的 id。
Match all
匹配全部文档:
GET member/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}不匹配任何文档:
GET member/_search
{
"query": {
"match_none":{}
}
}Span
主要用于处理跨度查询(即处理文本中词项的位置和距离)。它提供了一种低级别的查询接口,可以用于构建更复杂的查询,比如查询两个词项是否在一定的距离范围内出现。
首先创建数据:
PUT /span
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"field1": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
PUT /span/_doc/1
{
"field1": "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"
}
PUT /span/_doc/2
{
"field1": "The lazy dog sleeps in the sun"
}
PUT /span/_doc/3
{
"field1": "The quick brown cat jumps over the lazy dog"
}span term
查询包含 "quick" 的文档:
GET span/_search
{
"query": {
"span_term": {
"field1": {
"value": "quick"
}
}
}
}span first
查询开头不超过 5 个词的位置包含 "lazy" 的文档:
GET span/_search
{
"query": {
"span_first": {
"match": {
"span_term": {
"field1": "lazy"
}
},
"end": 5
}
}
}span near
搜索 "quick" 和 "fox" 在两个词距离之内的文档:
GET span/_search
{
"query": {
"span_near": {
"clauses": [
{
"span_term": {
"field1": "quick"
}
},
{
"span_term": {
"field1": "fox"
}
}
],
"slop": 2,
"in_order": true
}
}
}span not
搜索包含 "quick" 但不在 "fox" 和 "dog" 之间的文档:
GET span/_search
{
"query": {
"span_not": {
"include": {
"span_term": {
"field1": "quick"
}
},
"exclude": {
"span_near": {
"clauses": [
{
"span_term": {
"field1": "fox"
}
},
{
"span_term": {
"field1": "dog"
}
}
],
"slop": 5,
"in_order": true
}
}
}
}
}span or
搜索包含 "quick" 或 "lazy" 的文档:
GET span/_search
{
"query": {
"span_or": {
"clauses": [
{
"span_term": {
"field1": "quick"
}
},
{
"span_term": {
"field1": "lazy"
}
}
]
}
}
}span containing
搜索在 "quick" 和 "dog" 之间包含了 "fox" 且 "quick" 和 "dog" 间隔不超过六个词的文档:
GET span/_search
{
"query": {
"span_containing": {
"little": {
"span_term": {
"field1": "fox"
}
},
"big": {
"span_near": {
"clauses": [
{
"span_term": {
"field1": "quick"
}
},
{
"span_term": {
"field1": "dog"
}
}
],
"slop": 6,
"in_order": true
}
}
}
}
}span field masking
TODO:
span multi-term
TODO:
span within
TODO: