IO模型
IO模型
用什么样的通道进行数据的发送和接收,很大程度上决定了程序通信的性能。
Java BIO
同步并阻塞(传统阻塞型),服务器实现模式为一个连接一个线程,即客户端有连接请求时服务器端就需要启动一个线程进行处理如果这个连接不做任何事就会造成不必要的开销,适用于连接数目比较小且固定的架构,对服务器资源要求较高。
BIO 服务器示例
本示例使用 Telnet 做客户端,当然自己写也是可以的,服务端使用线程池为每个请求创建一个对应的处理线程,主线程循环监听请求。
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author ppg007
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021/8/11 16:34
*/
public class BIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() / 2
, Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
, 10L
, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10)
, new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy());
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8848);
System.out.println("server has started!");
while (true){
System.out.println("waiting for connection");
Socket accept = serverSocket.accept();//卡在此处
System.out.println("a client has connected!");
threadPoolExecutor.submit(()->{
handler(accept);
});
}
// 如果有客户端连接,就创建一个线程,与之通讯
}
private static void handler(Socket socket) {
char[] chars = new char[1024];
try(InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream,"GBK")) {//使用转换流支持Windows中文
while (true){
System.out.println("reading");
int len = inputStreamReader.read(chars);//卡在此处
if (len==-1){
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===>"+new String(chars,0,len));
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===>"+"disconnected");
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}在启动 Telnet 连接前,服务端在输出 server has started 和 waiting for connection 后就一直等待,卡在接受连接处,连接上后,每次发送内容结束后,都会卡在 read 处,这就是 BIO 中阻塞的体现,且通过线程名并通过多个 Telnet 客户端连接可以发现确实是一个线程对应一个连接。
Java NIO
同步非阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个线程处理多个请求,即客户端发送的连接请求都会注册到多路复用器上,多路复用器轮询连接,有 I/O 请求就进行处理,适用于连接数量多且连接比较短的架构,如聊天服务器、弹幕系统服务期间通讯等,jdk1.4 加入。
三大核心部分:
- Channel(通道)。
- Buffer(缓冲区)。
- Selector(选择器)。
NIO 是面向缓冲区、或者面向块编程的。数据读取到一个它稍后处理的缓冲区,需要时可在缓冲区前后移动,提高了处理过程中的灵活性。
- 每个 channel 对应一个 buffer(一一对应)。
- 一个 selector 对应一个线程,一个线程对应多个 selector。
- channel 注册到 selector 中。
- 程序切换到那个 channel 是由事件 Event 决定的。
- selector 会根据不同的事件在各个通道上进行切换。
- buffer 就是一个内存块,底层是数组。
- 数据读取、写入通过 buffer,buffer 可读可写,需要通过
flip()方法切换(与 BIO 本质的区别)。 - channel 是双向的,可以返回底层操作系统的情况。
- 常用 channel 类:
- FileChannel。
- DatagramChannel。
- ServerSocketChannel。
- SocketChannel。

读写Buffer:
IntBuffer intBuffer = IntBuffer.allocate(10);
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < intBuffer.capacity(); i++) {
intBuffer.put(random.nextInt(100));
}
// 切换为只读buffer,再调用put方法会抛出异常
// intBuffer.asReadOnlyBuffer();
// intBuffer.put(1);
// 读写切换,不写下方循环不会输出
intBuffer.flip();
while (intBuffer.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(intBuffer.get());
}通过 channel 将字符串写入文件:
String str="蚌埠住了";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("src/main/resources/1.txt");
FileChannel channel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes());
byteBuffer.flip();
channel.write(byteBuffer);
fileOutputStream.close();通过 channel 从文件中读取内容并输出:
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("src/main/resources/1.txt");
FileChannel channel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(12);
channel.read(byteBuffer);
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array()));
fileInputStream.close();通过 channel 结合 buffer 拷贝文件:
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("src/main/resources/1.txt");
FileChannel channel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("src/main/resources/2.txt");
FileChannel fileOutputStreamChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
while (channel.read(byteBuffer) !=-1){
byteBuffer.flip();
fileOutputStreamChannel.write(byteBuffer);
// 一下两句选择一句即可,清空缓冲区
// byteBuffer.flip();
byteBuffer.clear();
}
fileOutputStream.close();
fileInputStream.close();只使用 channel 复制文件:
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("src/main/resources/69.jpg");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("src/main/resources/69-1.jpg");
FileChannel source = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel dest = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
source.transferTo(0,source.size(),dest);
dest.close();
source.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
fileInputStream.close();MappedBuffer 直接修改文件内容:
// 直接在堆外内存修改,操作系统不需要拷贝一次
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile("src/main/resources/1.txt","rw");
FileChannel channel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
MappedByteBuffer map = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 100);//指定范围
map.put(0,(byte) 'q');
map.put(99,(byte) 'c');
// map.put(100,(byte) 'c');溢出异常
randomAccessFile.close();NIO 支持使用多个 buffer 进行读写操作:
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(8848);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress);
ByteBuffer[] byteBuffers = new ByteBuffer[2];
byteBuffers[0]=ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
byteBuffers[1]=ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
SocketChannel accept = serverSocketChannel.accept();
while (true){
long byteRead=0;
while (byteRead<8){
long read = accept.read(byteBuffers);
byteRead+=read;
System.out.println("read");
System.out.println(byteRead);
}
byteBuffers[0].flip();
byteBuffers[1].flip();
long byteWrite=0;
while (byteWrite<8){
long write = accept.write(byteBuffers);
byteWrite+=write;
System.out.println("write");
}
byteBuffers[0].clear();
byteBuffers[1].clear();
System.out.println(byteRead);
System.out.println(byteWrite);
}selector 能够检测多个注册通道上是否有事件发生,如果有事件发生就获取事件进行处理,从而做到一个线程管理多个通道。
- 当客户端连接时,会通过 ServerSocketChannel 的 accept 方法得到 SocketChannel,每个客户端都有一个 channel。
- selector 进行监听,select 方法返回有事件发生的通道个数。
- 将 SocketChannel 注册到 selector 上,一个 selector 可以注册多个 channel,通过
register方法。 - 注册后返回一个 SelectionKey 和指定的 selector 关联。
- 进一步得到各个 key。
- 通过 key 反向获取 channel。
- 通过得到的 channel 进行业务处理。
服务器代码示例:
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 得到一个选择器对象
Selector selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8848));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true){
// select有三个方法
// 无参方法是阻塞的
// 一个参数的方法是阻塞指定毫秒数
// selectNow不阻塞立刻返回
// 还有一个唤醒方法wakeup
if (selector.select(1000)==0){
System.out.println("服务器等待了一秒,无连接");
continue;
}
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
if (key.isAcceptable()){
SocketChannel accept = serverSocketChannel.accept();
accept.configureBlocking(false);
accept.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
}
if (key.isReadable()){
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println("客户端发来:"+new String(buffer.array()));
}
iterator.remove();
}
}客户端代码示例:
SocketChannel channel = SocketChannel.open();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8848);
if (!channel.connect(inetSocketAddress)){
while (!channel.finishConnect()){
System.out.println("客户端不阻塞");
}
}
String str="蚌埠住了";
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());
channel.write(buffer);
System.in.read();利用 NIO 实现在线群聊系统
服务端代码:
package groupchat;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author ppg007
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021/8/12 19:57
*/
public class Server {
// 服务端拥有selector
private Selector selector;
// 服务端channel
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
// 服务端监听端口
private static final int port=8848;
public Server() {
try {
// 初始化
this.selector=Selector.open();
this.serverSocketChannel= ServerSocketChannel.open();
this.serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
this.serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 监听连接事件
this.serverSocketChannel.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void listen(){
try {
while (true){
// 间隔两秒监听
int count = this.selector.select(2000);
if (count>0){
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = this.selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
// 如果可以连接
if (key.isAcceptable()){
// 创建连接channel
SocketChannel accept = this.serverSocketChannel.accept();
accept.configureBlocking(false);
// 注册到selector并监听读事件,是服务端读这个客户端可读
accept.register(this.selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println(accept.getRemoteAddress()+" 上线 ");
}else if(key.isReadable()){
// 如果可读就读取指定key对应的channel
read(key);
}
iterator.remove();
}
}else {
System.out.println("等待......");
}
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void read(SelectionKey key){
SocketChannel channel=null;
try {
channel= ((SocketChannel) key.channel());
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int count = channel.read(buffer);
if (count>0) {
String msg = new String(buffer.array());
System.out.println("收到客户端消息:"+msg);
// 转发给其他客户端
forward(msg,channel);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
try {
System.out.println(channel.getRemoteAddress()+" 离线了");
// 转发离线消息给其他客户端
forward(channel.getRemoteAddress()+ "离线了",channel);
// 取消注册
key.cancel();
// 关闭channel
channel.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void forward(String msg,SocketChannel channel) throws IOException {
System.out.println("服务器转发消息中");
// 获取所有注册的key
Set<SelectionKey> keys = this.selector.keys();
for (SelectionKey key : keys) {
Channel target = key.channel();
// 排除自己,不转发给自己
if (target instanceof SocketChannel && target!=channel){
SocketChannel destination = (SocketChannel) target;
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes());
destination.write(buffer);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Server server = new Server();
server.listen();
}
}客户端代码:
package groupchat;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author ppg007
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021/8/12 20:13
*/
public class Client {
// 指定主机地址
private static final String HOST="localhost";
// private static final String HOST="39.107.112.172";
// 指定主机端口号
private static final int PORT=8848;
// 定义selector用于监听事件,不用也可以,但是就要一直receive
private Selector selector;
// 定义channel
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
// 客户端名字
private String name;
public Client() throws IOException {
// 初始化
this.selector=Selector.open();
this.socketChannel=SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress(HOST,PORT));
this.socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
this.socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
this.name=this.socketChannel.getLocalAddress().toString();
System.out.println("客户端"+this.name+"准备好了");
}
public void send(String msg){
msg=this.name+" 说:\n"+msg;
try {
// 写入channel
this.socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes()));
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void receive(){
try {
int readChannels = this.selector.select();
if (readChannels>0){
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = this.selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
// 读取channel到buffer
if (key.isReadable()){
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
channel.read(buffer);
String msg = new String(buffer.array());
System.out.println(msg.trim());
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Client client = new Client();
// 用另一个线程循环接收
new Thread(()->{
while (true){
client.receive();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
// 主线程接收命令行输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()){
client.send(scanner.nextLine());
}
scanner.close();
}
}零拷贝
传统文件传输:数据读取和写入是从用户空间到内核空间来回复制,而内核空间的数据是通过操作系统层面的 I/O 接口从磁盘读取或写入。
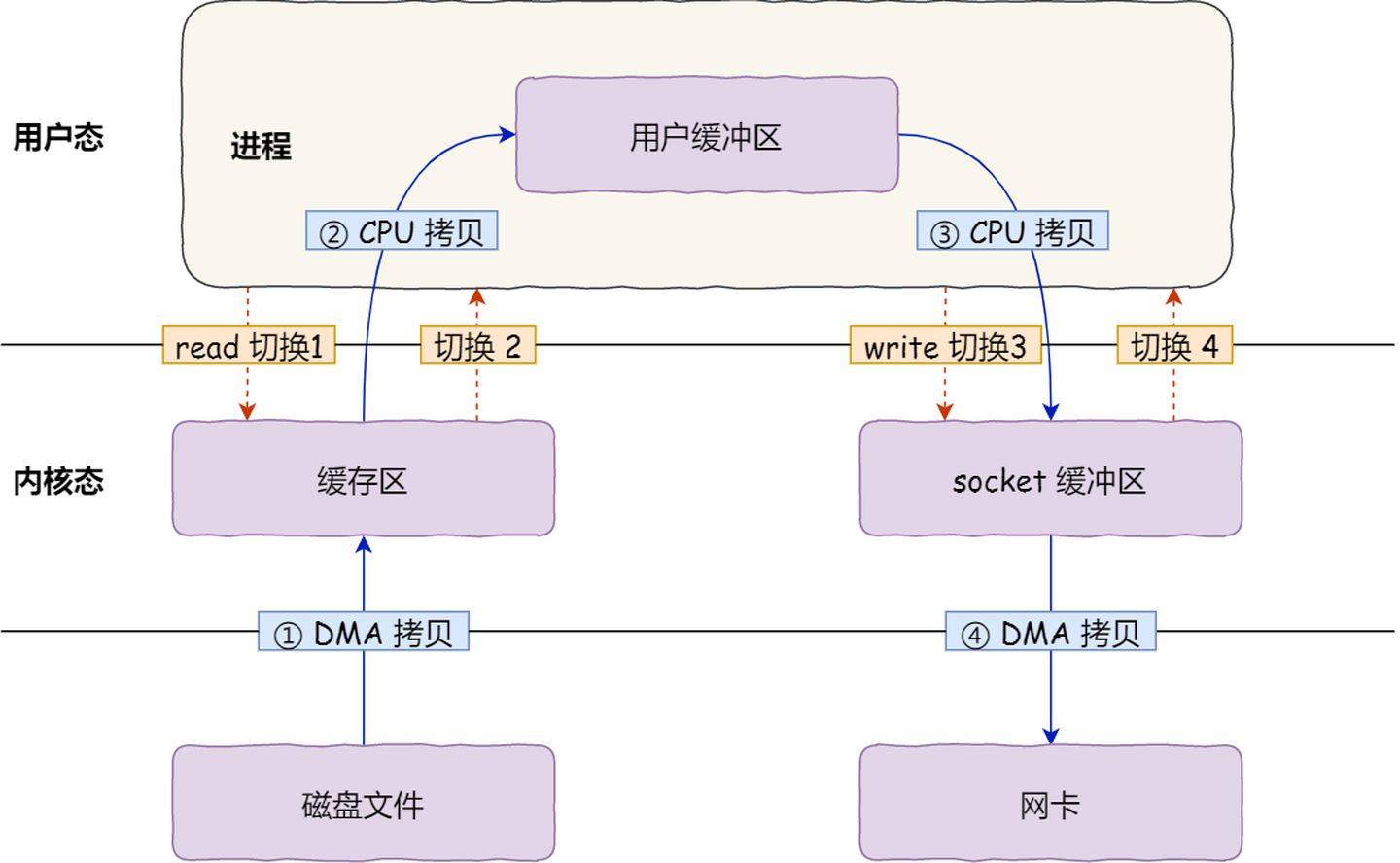
发生了 4 次用户态与内核态的上下文切换。
发生了 4 次数据拷贝:
- 第一次拷贝,把磁盘上的数据拷贝到操作系统内核的缓冲区里,这个拷贝的过程是通过 DMA 搬运的。
- 第二次拷贝,把内核缓冲区的数据拷贝到用户的缓冲区里,于是我们应用程序就可以使用这部分数据了,这个拷贝到过程是由 CPU 完成的。
- 第三次拷贝,把刚才拷贝到用户的缓冲区里的数据,再拷贝到内核的 socket 的缓冲区里,这个过程依然还是由 CPU 搬运的。
- 第四次拷贝,把内核的 socket 缓冲区里的数据,拷贝到网卡的缓冲区里,这个过程又是由 DMA 搬运的。
零拷贝技术实现的方式通常有 2 种:
mmap + write:
mmap()系统调用函数会直接把内核缓冲区里的数据「映射」到用户空间,这样,操作系统内核与用户空间就不需要再进行任何的数据拷贝操作。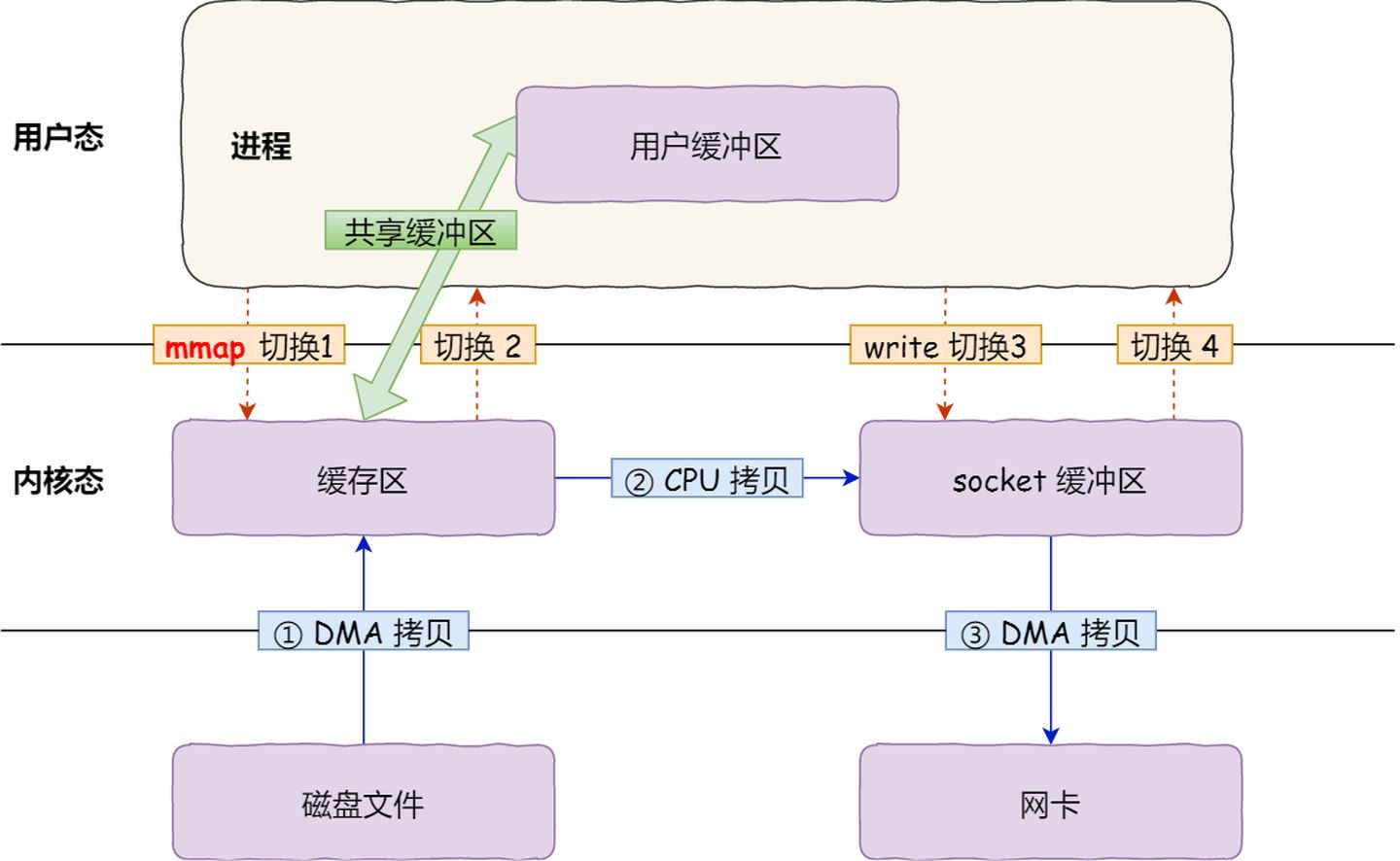
- 应用进程调用了
mmap()后,DMA 会把磁盘的数据拷贝到内核的缓冲区里。接着,应用进程跟操作系统内核「共享」这个缓冲区; - 应用进程再调用
write(),操作系统直接将内核缓冲区的数据拷贝到 socket 缓冲区中,这一切都发生在内核态,由 CPU 来搬运数据; - 最后,把内核的 socket 缓冲区里的数据,拷贝到网卡的缓冲区里,这个过程是由 DMA 搬运的。
减少一次数据拷贝的过程,仍然需要 4 次上下文切换,因为系统调用还是 2 次。
- 应用进程调用了
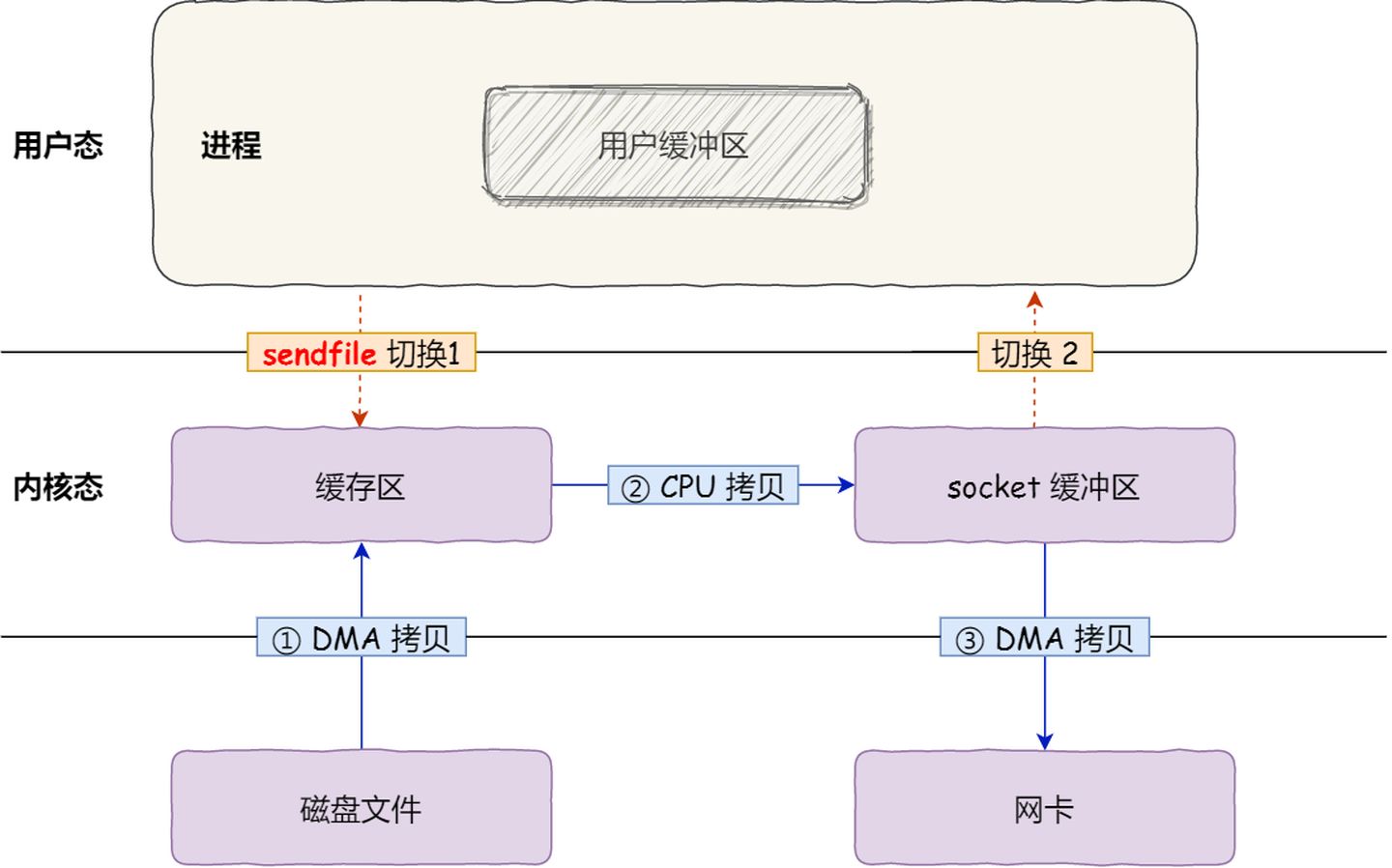
sendfile(linux2.1):
该系统调用,可以直接把内核缓冲区里的数据拷贝到 socket 缓冲区里,不再拷贝到用户态,这样就只有 2 次上下文切换,和 3 次数据拷贝。
从 Linux 内核
2.4版本开始起,对于支持网卡支持 SG-DMA 技术的情况下,sendfile()系统调用的过程发生了点变化,具体过程如下:- 第一步,通过 DMA 将磁盘上的数据拷贝到内核缓冲区里。
- 第二步,缓冲区描述符和数据长度传到 socket 缓冲区,这样网卡的 SG-DMA 控制器就可以直接将内核缓存中的数据拷贝到网卡的缓冲区里,此过程不需要将数据从操作系统内核缓冲区拷贝到 socket 缓冲区中,这样就减少了一次数据拷贝。
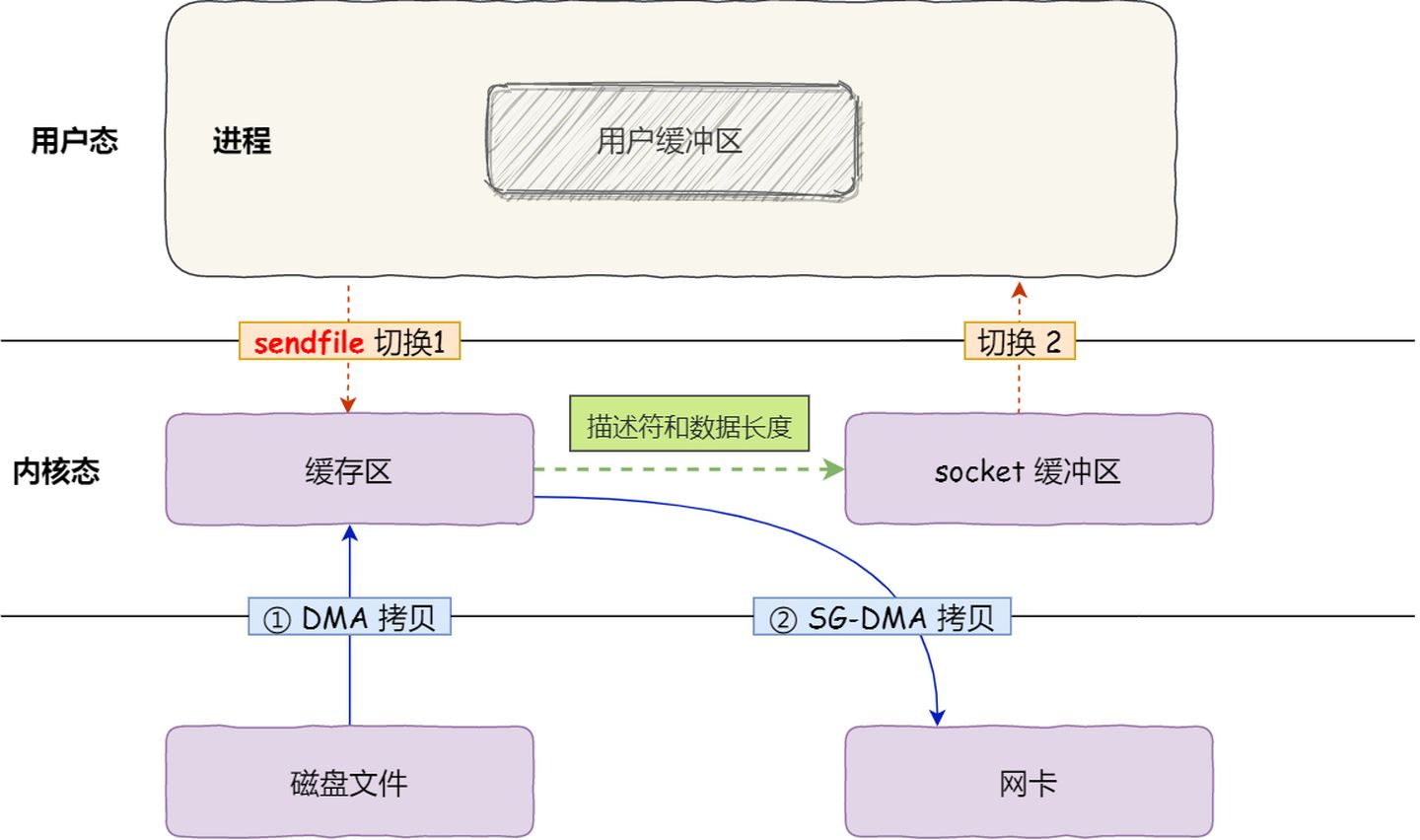
这就是所谓的零拷贝(*Zero-copy*)技术,因为我们没有在内存层面去拷贝数据,也就是说全程没有通过 CPU 来搬运数据,所有的数据都是通过 DMA 来进行传输的。。
零拷贝技术的文件传输方式相比传统文件传输的方式,减少了 2 次上下文切换和数据拷贝次数,只需要 2 次上下文切换和数据拷贝次数,就可以完成文件的传输,而且 2 次的数据拷贝过程,都不需要通过 CPU,2 次都是由 DMA 来搬运。
所以,总体来看,零拷贝技术可以把文件传输的性能提高至少一倍以上。
BIO 实现拷贝(文件大小 35.4MB)
服务端:
public class BIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket();
serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8848));
while (true){
Socket accept = serverSocket.accept();
InputStream inputStream = accept.getInputStream();
int len;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\Javaweb\\Netty-Learn\\NIO-Demo\\src\\main\\java\\zerocopy\\bio\\test.jpg");
while ((len=inputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){
fileOutputStream.write(buffer,0,len);
}
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
}客户端:
public class BIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long clientStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
Socket socket = new Socket();
socket.connect(new InetSocketAddress(8848));
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\Javaweb\\Netty-Learn\\NIO-Demo\\src\\main\\resources\\340.jpg");
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
long copyStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
while ((len=fileInputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){
outputStream.write(buffer,0,len);
}
long copyEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
fileInputStream.close();
socket.close();
long clientEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("发送文件耗时:"+(copyEnd-copyStart));
System.out.println("客户端总耗时:"+(clientEnd-clientStart));
}
}耗时情况:
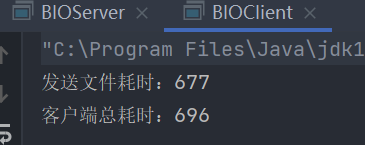
NIO 实现拷贝(文件大小 35.4MB)
服务端:
public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8848));
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\Javaweb\\Netty-Learn\\NIO-Demo\\src\\main\\java\\zerocopy\\nio\\test.jpg");
while (true){
FileChannel channel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
SocketChannel accept = serverSocketChannel.accept();
int len;
while ((len=accept.read(buffer))!=-1){
buffer.flip();
channel.write(buffer);
buffer.clear();
}
}
}
}客户端:
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long clientStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(8848));
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\Javaweb\\Netty-Learn\\NIO-Demo\\src\\main\\resources\\340.jpg");
FileChannel channel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
long size = channel.size();
double segment = size / (double) (8 * 1024 * 1024);
long copyStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
int i=0;
for (; i < (int)segment; i++) {
channel.transferTo(i*(8*1024*1024),(8*1024*1024),socketChannel);
}
if (segment!=(int)segment){
channel.transferTo(i*(8*1024*1024),size,socketChannel);
}
long copyEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
channel.close();
fileInputStream.close();
socketChannel.close();
long clientEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("发送文件耗时:"+(copyEnd-copyStart));
System.out.println("客户端总耗时:"+(clientEnd-clientStart));
}
}耗时情况:
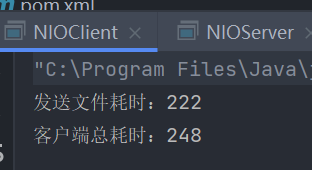
注意
Windows 环境中,调用一次 transfer 方法最大传输 8MB,需要分段,Linux 则不需要。
Java AIO
异步非阻塞,引入异步通道概念,采用 Proactor 模式,有效的请求才启动线程,特点:先由操作系统完成后才通知服务端程序启动线程去处理,适用于连接数较多且连接时间较长的应用,比如相册服务器,jdk1.7 加入。