synchronized 同步锁
2021/12/28大约 4 分钟
synchronized 同步锁
修饰方法,此时锁的是调用方法的对象
public class BuyTicket implements Runnable{
private static Integer ticketNum=10;
private boolean flag=true;
@Override
public void run() {
// ticketNum:监视器
while (flag){
try {
buy();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 锁方法或锁代码块
private synchronized void buy() throws InterruptedException {
if (ticketNum==0){
flag=false;
return ;
}
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"拿到"+ticketNum--);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuyTicket buyTicket = new BuyTicket();
new Thread(buyTicket,"user1").start();
new Thread(buyTicket,"user2").start();
new Thread(buyTicket,"user3").start();
}
}修饰变量
public class BuyTicket2 implements Runnable{
private static Integer num=10;
private boolean flag=true;
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuyTicket2 buyTicket = new BuyTicket2();
new Thread(buyTicket,"user1").start();
new Thread(buyTicket,"user2").start();
new Thread(buyTicket,"user3").start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (flag){
try {
buy();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void buy() throws InterruptedException {
// 获取资源
synchronized (num){
if (num>0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"拿到了"+num--);
}else {
flag=false;
}
}
}
}死锁
出现死锁的情况
public class DeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Consumer consumer1 = new Consumer();
Consumer consumer2 = new Consumer();
consumer1.setFlag(true);
consumer2.setFlag(false);
new Thread(consumer1,"consumer1").start();
new Thread(consumer2,"consumer2").start();
}
}
class SourceA{
}
class SourceB{
}
class Consumer implements Runnable{
private final static SourceA sourceA=new SourceA();
private final static SourceB sourceB=new SourceB();
private boolean flag;
@Override
public void run() {
try {
test();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void test() throws InterruptedException {
if (flag){
// 已经拥有一个资源时,再请求其他资源容易出现死锁
synchronized (sourceA){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获得了资源A");
Thread.sleep(1000);
synchronized (sourceB){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获得了资源B");
}
}
}
else {
synchronized (sourceB){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获得了资源B");
Thread.sleep(1000);
synchronized (sourceA){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获得了资源A");
}
}
}
}
public void setFlag(boolean flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
}死锁发现与解决
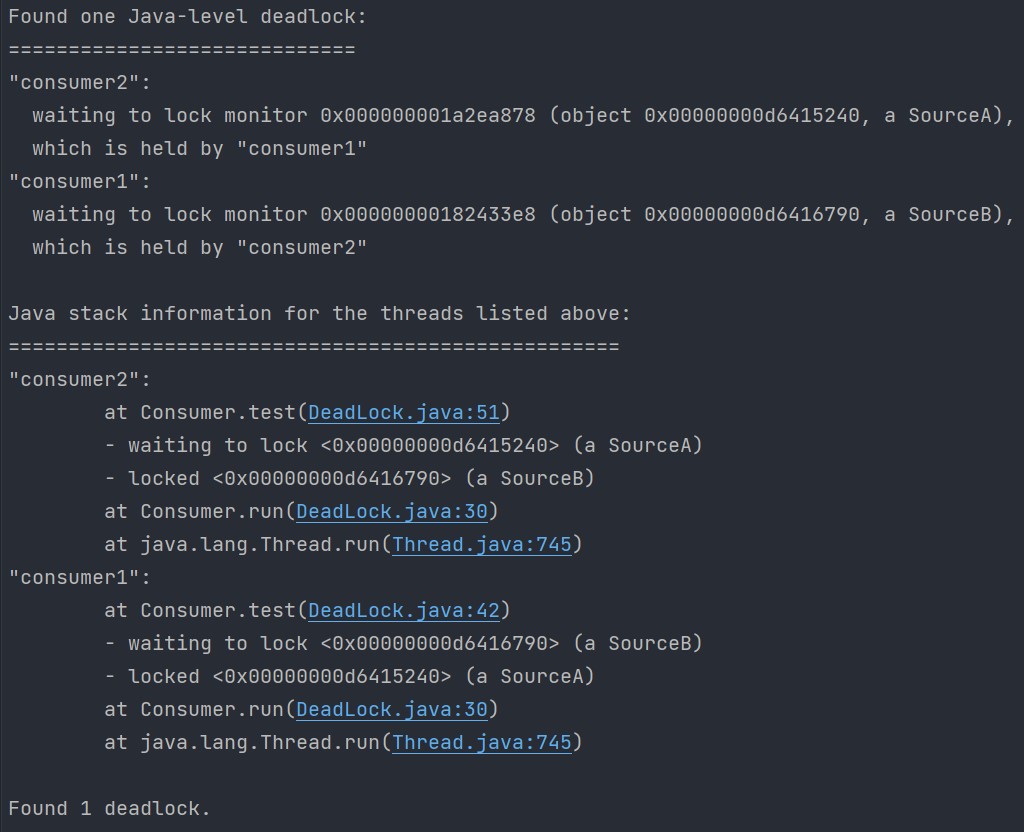
使用 Java bin 文件夹中的 jps 工具:jps -l 命令定位进程号。

使用 jstack [进程号] 查看进程堆栈找到死锁问题。
生产者消费者问题
管程法
synchronized 实现
管道:
public class Pool extends AbstractPool{
private Product[] products=new Product[5];
private int length=-1;
@Override
public void add(Product product){
synchronized (products){
// 等待总是应该出现在循环中,防止虚假唤醒
while (length==4){
try {
System.out.println("仓库已满");
products.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
++length;
products[length]=product;
products.notifyAll();
}
}
@Override
public Product get(){
synchronized (products){
while (length==-1){
try {
System.out.println("仓库为空");
products.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Product product = products[length];
length--;
products.notifyAll();
return product;
}
}
}生产者:
public class Provider extends Thread{
private AbstractPool pool;
public Provider(AbstractPool pool) {
this.pool = pool;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
pool.add(new Product(i));
System.out.println("生产了第"+i+"个产品");
}
}
}消费者:
public class Consumer extends Thread{
private AbstractPool pool;
public Consumer(AbstractPool pool) {
this.pool = pool;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("消费了第"+pool.get().getId()+"个产品");
}
}
}wait 方法:
该线程释放此监视器的所有权,并等待另一个线程通知等待该对象监视器的线程通过调用 notify 方法或 notifyAll 方法 notifyAll 。 然后线程等待,直到它可以重新获得监视器的所有权并恢复执行。
使用 PV 操作实现
public class PoolC extends AbstractPool{
private static LinkedList<Product> list=new LinkedList<>();
private static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 同步信号量
private Condition empty = lock.newCondition();
private Condition full = lock.newCondition();
@Override
public void add(Product product) {
try {
lock.lock();
while (list.size()!=0){
empty.await();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
list.add(new Product(i));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("生产了产品:"+i);
}
full.signal();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public Product get() {
try {
lock.lock();
while (list.size()!=5){
full.await();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("消费了产品:"+list.pop().getId());
}
empty.signal();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return null;
}
}信号灯法
来判断一个标志位 flag,如果为 true,就让他等待、如果为 false,就让他去通知另外一个人、把两人衔接起来。
package com.macro.mall.bo;
//测试生产者消费者问题2:信号灯法,通过标志位解决
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TV tv = new TV();
new Player(tv).start();
new Watcher(tv).start();
}
}
//生产者-->演员
class Player extends Thread {
TV tv;
public Player(TV tv) {
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
this.tv.play("什么是快乐星球");
} else {
this.tv.play("如果你想知道什么是快乐星球的话,那我就带你研究研究");
}
}
}
}
//消费者-->观众
class Watcher extends Thread {
TV tv;
public Watcher(TV tv) {
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
tv.watch();
}
}
}
//产品-->节目
class TV {
//演员表演,观众等待 T
//观众观看,演员等待 F
String voice; // 表演的节目
boolean flag = true;
//表演
public synchronized void play(String voice) {
if (!flag) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("演员表演了:" + voice);
//通知观众观看
this.notifyAll();
this.voice = voice;
this.flag = !this.flag;
}
//观看
public synchronized void watch() {
if (flag) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("观看了:" + voice);
//通知演员表演
this.notifyAll();
this.flag = !this.flag;
}
}