代理模式
2021/12/26大约 2 分钟
代理模式
静态代理
角色
- 抽象角色:一般用抽象类或接口。
- 真实角色:被代理的角色。
- 代理角色:代理真实角色的角色,一般有附属操作。
- 客户:访问代理对象的人。
代码过程
- 接口。
- 真实角色。
- 代理角色。
- 客户端访问代理角色。
代理模式优点
- 使真实角色的操作更加纯粹,不用去关注一些公共的业务。
- 实现了业务的分工。
- 公共业务发生扩展时,便于集中管理。
静态代理模式缺点
每个真实角色都会有一个代理角色,代码量翻倍,开发效率降低。
动态代理
- 动态代理的代理类是动态生成的。
- 动态代理分类:
- 基于接口的动态代理:JDK动态代理。InvocationHandler
- 基于类的动态代理:CGLIB。
- Java字节码实现:Javassist。
InvocationHandler 是由代理实例的调用处理程序实现的接口。
每个代理实例都有一个关联的调用处理程序。 当在代理实例上调用方法时,方法调用将被编码并分派到其调用处理程序的 invoke 方法。
实现类:Proxy.
InvocationHandler handler = new MyInvocationHandler(...);
Class<?> proxyClass = Proxy.getProxyClass(Foo.class.getClassLoader(), Foo.class);
Foo f = (Foo) proxyClass.getConstructor(InvocationHandler.class).newInstance(handler);或
Foo f = (Foo) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Foo.class.getClassLoader(),new Class<?>[] { Foo.class },handler);方法: 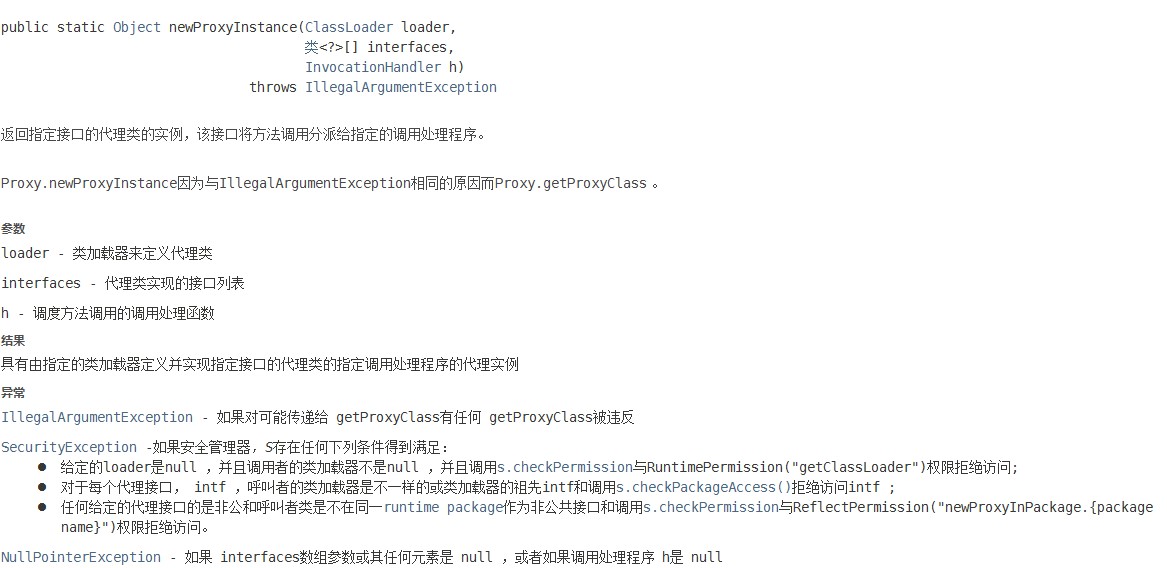
示例代码(中介租房)
- 要代理的接口:
public interface Rent {
/**
* test
*/
void rent();
}- 被代理的真实角色(要实现被代理的接口):
public class Host implements Rent{
public void rent() {
System.out.println("房东出租");
}
}- 代理类:
public class ProxyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
//要被代理的真实角色
private Object target;
public void setTarget(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
//动态生成代理类
public Object getProxy(){
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(),target.getClass().getInterfaces(),this);
}
//处理代理的实例,返回结果
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
see();
System.out.println(method.getName());
return method.invoke(target,args);
}
//自定义的方法
public void see(){
System.out.println("看房");
}
}- 入口方法:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//要代理的真实角色
Host host=new Host();
//创建代理类对象
ProxyInvocationHandler proxyInvocationHandler = new ProxyInvocationHandler();
//设置要代理的对象
proxyInvocationHandler.setTarget(host);
//动态生成代理类
Rent proxy= (Rent) proxyInvocationHandler.getProxy();
//调用相关方法
proxy.rent();
}
}