Vuex
Vuex
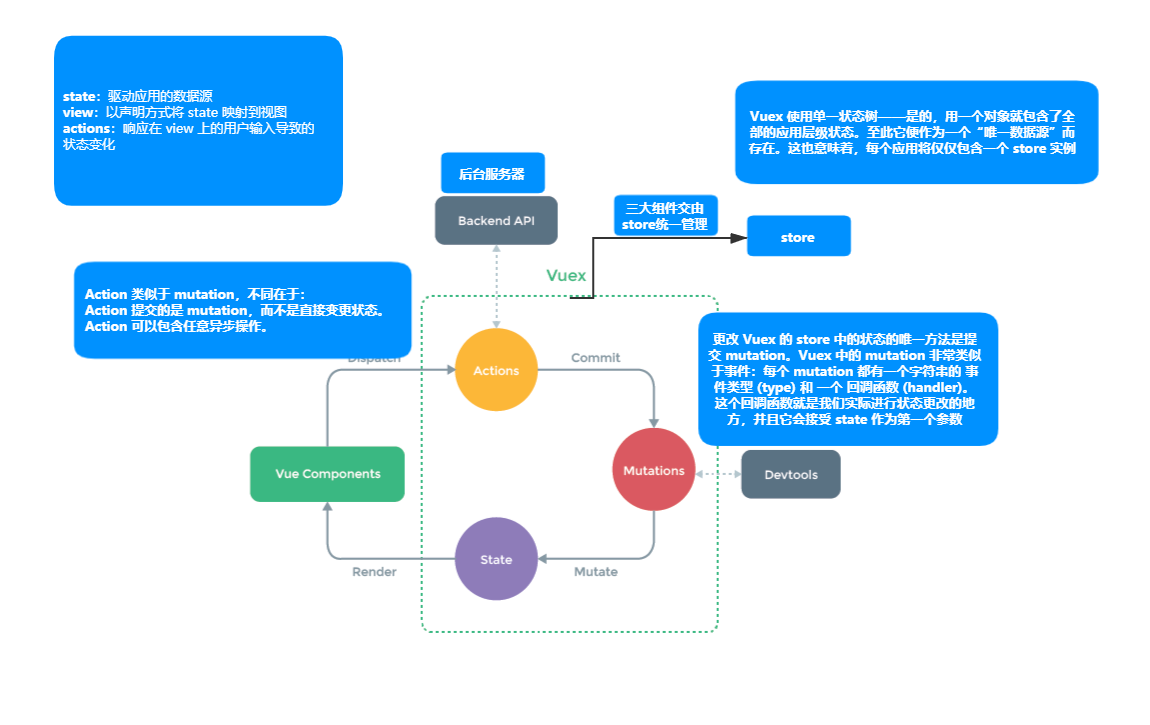
Vuex 工作原理
配置 Vuex 环境
安装 Vuex:
npm install vuex --save在 src 文件夹中创建 store 文件夹,并在其中创建 index.js 文件,编写如下内容:
'use strict';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import Vue from 'vue';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const actions = {};
const mutations = {};
const state = {};
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state,
});注意
Vue.use() 必须要写在创建 store 对象前,如果写在 main.js 中然后引用 index.js,且使用了 Vue-CLI 脚手架,则脚手架会先执行所有的 import 语句,导致导入 index.js 前没有执行 Vue.use() 发生报错,所以要写在 index.js 中。
main.js 引入 index.js:
import Vue from 'vue';
import App from './App.vue';
import store from './store';
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
store,
}).$mount('#app');求和案例
求和子模块:
通过 store 的 dispatch() 方法触发 actions:
<template>
<div>
<h2>当前n为{{ n }}</h2>
<select v-model.number="step">
<option value="1">1</option>
<option value="2">2</option>
<option value="3">3</option>
</select>
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
<button @click="incrementOdd">当前求和为奇数才加</button>
<button @click="incrementWait">延迟两秒加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Counter',
data() {
return {
step: 1,
};
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.$store.dispatch('add', this.step);
},
decrement() {
this.$store.dispatch('sub', this.step);
},
incrementOdd() {
this.$store.dispatch('addOdd', this.step);
},
incrementWait() {
this.$store.dispatch('addWait', this.step);
},
},
computed: {
n: {
get() {
return this.$store.state.n;
},
},
},
};
</script>actions 和 mutations:
const actions = {
// context与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性
add(context, data) {
context.commit('ADD', data);
},
sub(context, data) {
context.commit('SUB', data);
},
addOdd(context, data) {
//在actions中再次分发给其他action并接受返回值,返回值是promise类型
context.dispatch('isOdd', context.state.n).then(result => {
console.log(result);
if (result) {
context.commit('ADD', data);
}
});
},
addWait(context, data) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('ADD', data);
}, 2000);
},
isOdd(context, data) {
return data % 2 !== 0;
},
};
const mutations = {
ADD(state, data) {
state.n += data;
},
SUB(state, data) {
state.n -= data;
},
};
const state = {
n: 0,
};getters
当要获取加工后的 state 数据时使用:
<h2>当前n的算术平方根为{{sqrtN}}</h2>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Counter',
computed: {
sqrtN: {
get() {
return this.$store.getters.process;
},
},
},
};
</script>index.js:
const getters = {
process(state) {
return Math.sqrt(state.n);
},
};
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state,
getters,
});getters 定义与计算属性类似,但是能做到全局复用,计算属性只能组件内复用,都通过返回值获取属性值。
mapState 与 mapGetters
在组件中频繁写 this.$store.state 过于繁琐,使用 mapState 与 mapGetters 可以简化代码。
首先在组件中引入 mapState 和 mapGetters:
import { mapState, mapGetters } from 'vuex';在计算属性中使用,前面加三个点表示以对象形式加入:
computed: {
// 对象写法
// ...mapState({n:'n',name:'name',age:'age'})
// ...mapState({n:state => state.n,name:state => state.name,age:state => state.age})
...mapState({
n(state) {
return state.n;
},
name(state) {
return state.name;
},
age(state) {
return state.age*100;
}
}),
// 数组写法
// ...mapState(['n','name','age'])
...mapGetters({sqrtN:'process'})
// ...mapGetters(['process'])
}mapState 有四种写法:
- 对象写法,对象中是键值对,键为需要的计算属性名,值必须用引号,表示在
state中对应数据的名字。 - 对象写法,对象中是键值对,键为需要计算的属性名,值为箭头函数,参数为
state。 - 对象写法,对象中是函数,函数参数为
state,可以进行复杂处理。 - 数组写法,仅适用于需要的计算属性与
state中属性重名的情况。
mapGetters 有两种写法:
- 数组写法,仅适用于需要的计算属性与
getters中函数重名的情况。 - 对象写法,对象中是键值对,键为需要的计算属性,值为
getters中对应函数的名字。
mapActions 与 mapMutations
在组件中频繁创建方法调用 actions 或 mutations 非常繁琐,使用 mapActions 和 mapMutations 可以简化代码。
首先在组件中引入 mapActions 和 mapMutations:
import { mapActions, mapMutations } from 'vuex';在 methods 中应用:
methods: {
// 调用时传参
...mapMutations({increment:'ADD',decrement:'SUB'}),
// 调用时传参
// ...mapMutations(['ADD','SUB']),
// 调用时要传参数
...mapActions({incrementOdd:'addOdd', incrementWait:'addWait'})
// 调用时要传参数
// ...mapActions(['addWait','addOdd'])
},mapActions 有两种写法:
- 对象写法,键为要定义的方法名,值为 actions 中定义的方法。
- 数组写法,仅适用于要定义的方法名和定义在 actions 中的方法同名的情况。
mapMutations 有两种写法:
- 对象写法,键为要定义的方法名,值为 mutations 中已定义的方法名。
- 数组写法,仅适用于要定义的方法名和定义在 mutations 中的方法同名的情况。
提示
mapActions 和 mapMutations 不论使用哪种写法,都必须在调用时传入参数,否则默认参数是 event。
示例:
<button @click="incrementOdd(step)"></button>
<button @click="incrementWait(step)"></button>多组件共享数据
在此前计数器组件基础上,添加人员列表组件,完成人员列表组件能看到计数器当前值,计数器组件能看到人员列表长度。
在 index.js 中给 actions 添加方法:
addPerson(context,data) {
if (data.trim()===''){
alert('请输入内容')
}else {
context.commit('ADD_PERSON',data)
}
}在mutations中添加:
ADD_PERSON(state,data){
state.people.unshift(data)
alert('陈坤')
}为 state 添加一个人员数组:
const state = {
n: 0,
name: 'PPG',
age: 21,
people: [],
};在计数器组件模板中添加:
<h4>当前人员列表中人数为:{{number}}</h4>其中 number 是计算属性,定义如下:
computed: {
...mapState({
n(state) {
return state.n;
},
name(state) {
return state.name;
},
age(state) {
return state.age;
},
number(state) {
return state.people.length;
}
}),创建人员列表组件:
<template>
<div>
<div>
<input
v-model="temp"
type="text"
placeholder="输入姓名,回车确认"
@keydown.enter="addPerson(temp)"
/>
</div>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in people" :key="index">
{{ item }}
</li>
</ul>
<div>计数器组件的当前值为:{{ n }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapActions, mapState } from 'vuex';
export default {
name: 'People',
data() {
return {
temp: '',
};
},
methods: {
...mapActions(['addPerson']),
},
computed: {
...mapState(['people', 'n']),
},
//通过监视people数组变化清空输入框
watch: {
people: {
deep: true,
handler() {
this.temp = '';
},
},
},
};
</script>模块化
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割。
将上一个部分中人员列表和计数器的 vuex 拆分,可以写在 index.js 中,也可以每个模块拆分出一个文件然后 index 中进行引用。
people.js:
'use strict';
export default {
namespaced: true,
actions: {
addPerson(context, data) {
if (data.trim() === '') {
alert('请输入内容');
} else {
context.commit('ADD_PERSON', data);
}
},
},
mutations: {
ADD_PERSON(state, data) {
state.people.unshift(data);
alert('陈坤');
},
},
getters: {},
state: {
people: [],
},
};counter.js:
'use strict';
export default {
namespaced: true,
actions: {
addOdd(context, data) {
context.dispatch('isOdd', context.state.n).then(result => {
if (result) {
context.commit('ADD', data);
}
});
},
addWait(context, data) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('ADD', data);
}, 2000);
},
isOdd(context, data) {
return data % 2 !== 0;
},
},
mutations: {
ADD(state, data) {
state.n += data;
},
SUB(state, data) {
state.n -= data;
},
},
getters: {
process(state) {
return Math.sqrt(state.n);
},
},
state: {
n: 0,
name: 'PPG',
age: 21,
},
};index.js:
'use strict';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import Vue from 'vue';
import counterOptions from '@/store/counter';
import peopleOptions from '@/store/people';
Vue.use(Vuex);
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
peopleOptions,
counterOptions,
},
});在分模块中添加 namespaced 属性开启命名空间,如果不写,默认为 false,每个模块中的 actions 和 mutations 为全局可用,state 不是全局可用,要访问可以使用模块名前缀。
counter.vue:
<script>
import { mapState, mapGetters } from 'vuex';
import { mapActions, mapMutations } from 'vuex';
export default {
name: 'Counter',
data() {
return {
step: 1,
};
},
methods: {
...mapMutations('counterOptions', { increment: 'ADD', decrement: 'SUB' }),
...mapActions('counterOptions', { incrementOdd: 'addOdd', incrementWait: 'addWait' }),
},
computed: {
...mapState('counterOptions', {
n(state) {
return state.n;
},
name(state) {
return state.name;
},
age(state) {
return state.age;
},
}),
...mapState('peopleOptions', {
number(state) {
return state.people.length;
},
}),
...mapGetters('counterOptions', { sqrtN: 'process' }),
},
};
</script>people.vue:
<script>
import { mapActions, mapState } from 'vuex';
export default {
name: 'People',
data() {
return {
temp: '',
};
},
methods: {
...mapActions('peopleOptions', ['addPerson']),
},
computed: {
...mapState('peopleOptions', ['people']),
...mapState('counterOptions', ['n']),
},
watch: {
people: {
deep: true,
handler() {
this.temp = '';
},
},
},
};
</script>在所有的 map 辅助函数中第一个参数传入在 index.js 中注册的模块名即可。
如果不使用辅助函数,要注意访问的路径为命名空间/getters 方法名。
例如通过如下方式在 counter.vue 中访问。
//返回值就是getters对应函数的结果
this.$store.getters['counterOptions/process'];对于模块内部的 action,局部状态通过 context.state 暴露出来,根节点状态则为 context.rootState。
对于模块内部的 getter,根节点状态会作为第三个参数暴露出来。